Ansible As A Source To CMDB
The Ansible server contains valuable data about the current configuration state at the operating system level. In addition, Ansible can be configured to retrieve custom, application-specific facts. This guide explains how to add Ansible Facts integration to Cloudaware.
Ansible variables
Ansible collects data from hosts and stores it as Ansible variables. These variables can be loaded into CMDB through Cloudaware’s Ansible integration. Cloudaware supports native Ansible variables, custom variables, factor_*, and ohai_* variables.
Benefits of Ansible data in CMDB
Detect instances not connected to Ansible
Track the last successful Ansible execution on a host
Enrich CMDB with OS and application-level data
Run reports on variables
Monitor changes in variables
Trigger workflows and approval processes based on variable values
Convert facts into instance attributes
Add an Ansible Facts integration
Prerequisites
Upload AWS* EC2 instance facts to AWS S3 bucket accessible by Cloudaware.
*Although Ansible supports multi-cloud, the Cloudaware integration currently supports only AWS.
Log in to Cloudaware → Admin.
Find Ansible Facts in DevOps integrations. Click +ADD.

Fill out the form:
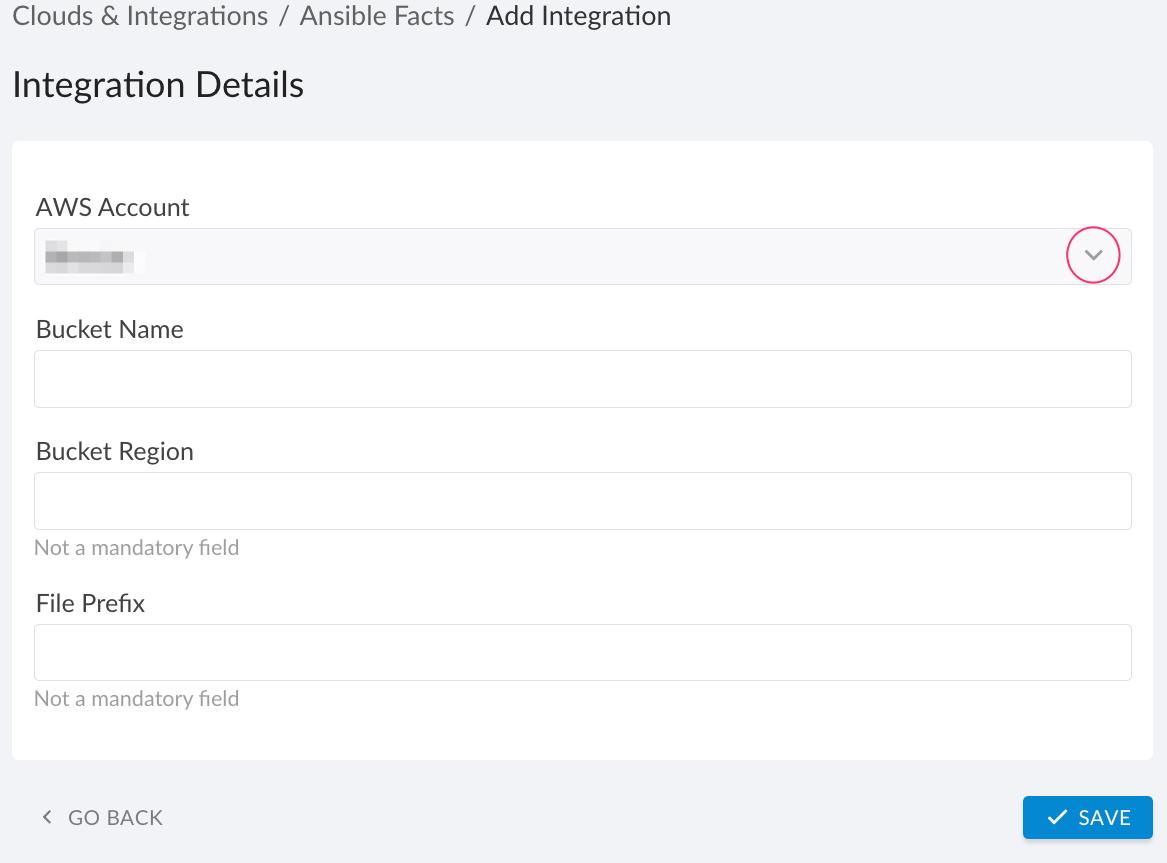
WHERE
AWS Account – select one from the drop-down list
Bucket Name – the name of the S3 bucket that stores the uploaded EC2 instance facts
Bucket Region – specify the AWS region where the S3 bucket resides
File Prefix – the path prefix within the bucket for Cloudaware to read the uploaded facts
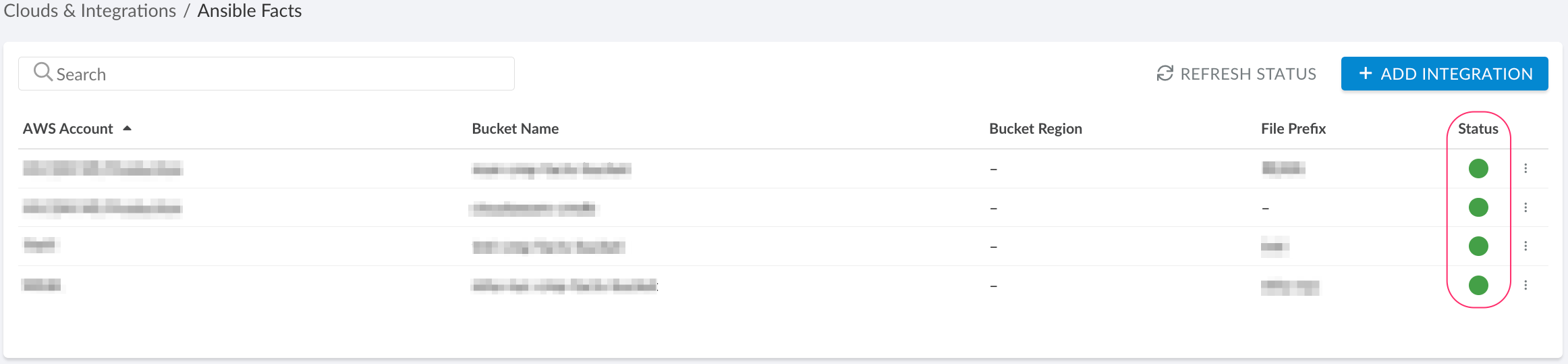
Click SAVE.A green light in the ‘Status’ column indicates successful configuration. If the light is red, contact support@cloudaware.com.
Facts are displayed on AWS EC2 instances in the Cloudaware CMDB.
Alternatively, install the Ansible-to-S3 adapter on the Ansible server. Instructions are available here.
List of Ansible-specific fields in CMDB
Object | Fields |
|---|---|
AWS EC2 Instance | Last Ansible Fact Update (Date/Time) |
